Just 3 problems left in the book, all to do with fault detection.
The problem: Fault Detection in Logic Circuits. This is problem MS17 in the appendix.
The description: Given a directed graph G=(V,A) representing a circuit as follows:
- All vertices with indegree 0 are “inputs”. There can be several inputs.
- Exactly one vertex, v* (called “z” in the paper), is the “output”. This will hold the result of the circuit.
- Each other vertex is either an AND, OR, or NOT vertex. AND and OR vertices have indegree 2, and NOT vertices have indegree 1.
We’re given a subset V’ of V that we wish to test. We are testing for “stuck-at” faults, where the output of the vertex is always the same regardless of the input. Can we create a set of input tests that will detect a fault at any vertex in V’?
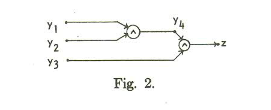
Example: Here is a circuit example from the paper by Ibarra and Sahni:
Our V’ is the set of y vertices, plus z (the paper uses z instead of v* to denote the output vertex).
A test set does not have to isolate which vertex is wrong. We just want to know that if a vertex is stuck at 0 or 1, our tests will be wrong someplace.
So, a test set of setting all inputs to 1, will, if the output is 0, tell us that there is a stuck at 0 fault in one of the 4 vertices we are testing. It will not tell us about any stuck at 1 faults, because the output should be 1 anyway.
Notice that we can’t just test setting all inputs to 0 and looking for a 1 and use that as our test to see if a stuck at 1 fault at any vertex, because the only way to get a 1 from that input would b if z itself were wrong, or if there were more than one fault, and we are only detecting single faults. So that test only tells us about z. In order to test the y vertices, we’ll need more tests.
If we set y1 =0, y2=1, and y3=1, the output of the circuit (and all gates) should be 0. If we get a 1, we must have a stuck at 1 fault on y1, y4, or z.
Similarly, if we set y1=1, y2=0, and y3 = 1, an output of 1 from the circuit (instead of 0) tells us that a stuck at 1 fault is in either z, y2, or y4.
Finally, a test of y1=1, y2=1, and y3=0, and an output of 1 tells us that a stuck at one fault is in either z, y3, or y4.
Reduction: The paper by Ibarra and Sahni reduce from DNF Non-Tautology. So we start with a formula with clauses B1..Bk, and variables x1..xn.
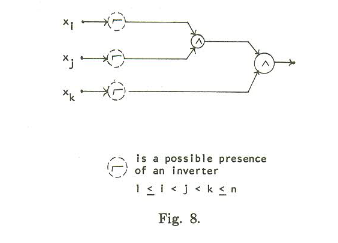
Each clause gets its own circuit:
The inputs xi, xj, and xk correspond to variables in the clause. If the literal in the clause is negated, we add the not gate. We’ve built the test set for this above (well, the version where there were no negations, but the other cases are similar).
We then hook up each of these clauses with OR gates. B1 and B2’s outputs get OR-ed together. The output of that gets OR-ed with B3’s output, and so on. The paper shows that once you have test sets for the inner clauses, you can test this larger circuit with 5k total tests. First, we validate that all of these tests make at least one clause return true. If they don’t, then we have found a way to make the formula not be a tautology, so we return “no” and stop.
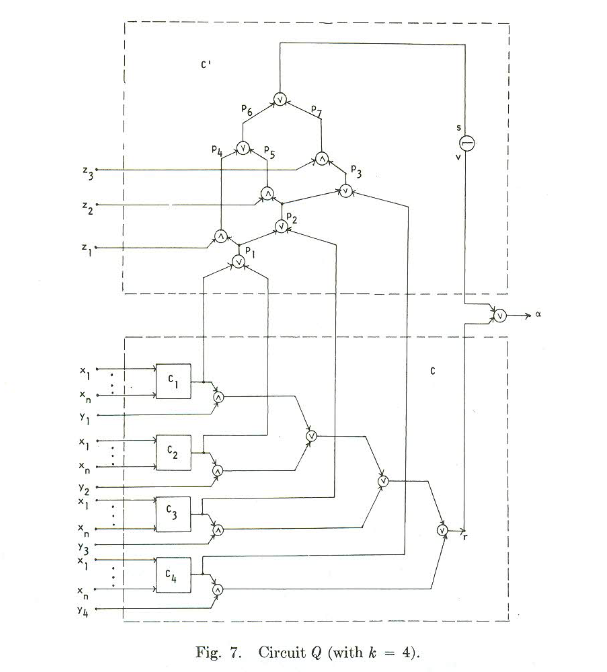
Assuming we don’t have that situation we keep going and extend the circuit to something more complicated:
(This is a small example for 4 clauses. The paper also describes a more general version)
The bottom part of the figure is the circuit we had originally for all of the clauses. The top part is fixed, and only defined by the number of clauses in the formula.
The paper proves that we can only have a legal test set for this circuit if and only if there is a way to set the variables in x so that all of the Ci circuits output 0. If that happens, we do not have a tautology. The idea is that if we do have a tautology, then every setting of the variables will make one of the Ci circuits output 1, and so you will never be able to detect a stuck at 1 fault in P3, since P3 will be 1 if any of the clauses output 1. It’s a little harder to show that if we can make all of the clauses output 0, we can detect all faults, but the paper lists out how to make those tests.
Difficulty: 8. I had a hard time following all of the circuit stuff. I do wonder if an easier reduction is out there.
 ‘
‘